問題
假設你在存檔中有成千上萬的文檔,其中許多是彼此重復的�����,即使文檔的內容相同����,標題不同�����。 現在想象一下��,現在老板要求你通過刪除不必要的重復文檔來釋放一些空間。
問題是:如何過濾標題足夠相似的文本��,以使內容可能相同����? 接下來,如何實現此目標�����,以便在完成操作時不會刪除過多的文檔�����,而保留一組唯一的文檔����? 讓我們用一些代碼使它更清楚:
titles = [
"End of Year Review 2020",
"2020 End of Year",
"January Sales Projections",
"Accounts 2017-2018",
"Jan Sales Predictions"
]
# Desired output
filtered_titles = [
"End of Year Review 2020",
"January Sales Projections",
"Accounts 2017-2018",
]
根據以上的問題�����,本文適合那些希望快速而實用地概述如何解決這樣的問題并廣泛了解他們同時在做什么的人!
接下來�����,我將介紹我為解決這個問題所采取的不同步驟��。下面是控制流的概要:
預處理所有標題文本
生成所有標題成對
測試所有對的相似性
如果一對文本未能通過相似性測試��,則刪除其中一個文本并創建一個新的文本列表
繼續測試這個新的相似的文本列表,直到沒有類似的文本留下
用Python表示��,這可以很好地映射到遞歸函數上!
代碼
下面是Python中實現此功能的兩個函數��。
import spacy
from itertools import combinations
# Set globals
nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_md")
def pre_process(titles):
"""
Pre-processes titles by removing stopwords and lemmatizing text.
:param titles: list of strings, contains target titles,.
:return: preprocessed_title_docs, list containing pre-processed titles.
"""
# Preprocess all the titles
title_docs = [nlp(x) for x in titles]
preprocessed_title_docs = []
lemmatized_tokens = []
for title_doc in title_docs:
for token in title_doc:
if not token.is_stop:
lemmatized_tokens.append(token.lemma_)
preprocessed_title_docs.append(" ".join(lemmatized_tokens))
del lemmatized_tokens[
:
] # empty the lemmatized tokens list as the code moves onto a new title
return preprocessed_title_docs
def similarity_filter(titles):
"""
Recursively check if titles pass a similarity filter.
:param titles: list of strings, contains titles.
If the function finds titles that fail the similarity test, the above param will be the function output.
:return: this method upon itself unless there are no similar titles; in that case the feed that was passed
in is returned.
"""
# Preprocess titles
preprocessed_title_docs = pre_process(titles)
# Remove similar titles
all_summary_pairs = list(combinations(preprocessed_title_docs, 2))
similar_titles = []
for pair in all_summary_pairs:
title1 = nlp(pair[0])
title2 = nlp(pair[1])
similarity = title1.similarity(title2)
if similarity > 0.8:
similar_titles.append(pair)
titles_to_remove = []
for a_title in similar_titles:
# Get the index of the first title in the pair
index_for_removal = preprocessed_title_docs.index(a_title[0])
titles_to_remove.append(index_for_removal)
# Get indices of similar titles and remove them
similar_title_counts = set(titles_to_remove)
similar_titles = [
x[1] for x in enumerate(titles) if x[0] in similar_title_counts
]
# Exit the recursion if there are no longer any similar titles
if len(similar_title_counts) == 0:
return titles
# Continue the recursion if there are still titles to remove
else:
# Remove similar titles from the next input
for title in similar_titles:
idx = titles.index(title)
titles.pop(idx)
return similarity_filter(titles)
if __name__ == "__main__":
your_title_list = ['title1', 'title2']
similarty_filter(your_title_list)
第一個是預處理標題文本的簡單函數;它刪除像' the '�����, ' a ', ' and '這樣的停止詞,并只返回標題中單詞的引理。
如果你在這個函數中輸入“End of Year Review 2020”,你會得到“end year review 2020”作為輸出;如果你輸入“January Sales Projections”����,你會得到“january sale projection”�����。
它主要使用了python中非常容易使用的spacy庫.
第二個函數(第30行)為所有標題創建配對,然后確定它們是否通過了余弦相似度測試����。如果它沒有找到任何相似的標題����,那么它將輸出一個不相似標題的列表����。但如果它確實找到了相似的標題,在刪除沒有通過相似度測試的配對后�����,它會將這些過濾后的標題再次發送給它自己����,并檢查是否還有相似的標題。
這就是為什么它是遞歸的!簡單明了,這意味著函數將繼續檢查輸出����,以真正確保在返回“最終”輸出之前沒有類似的標題�����。
什么是余弦相似度?
但簡而言之,這就是spacy在幕后做的事情……
首先,還記得那些預處理過的工作嗎?首先,spacy把我們輸入的單詞變成了一個數字矩陣����。
一旦它完成了����,你就可以把這些數字變成向量��,也就是說你可以把它們畫在圖上����。
一旦你這樣做了��,計算兩條直線夾角的余弦就能讓你知道它們是否指向相同的方向�����。
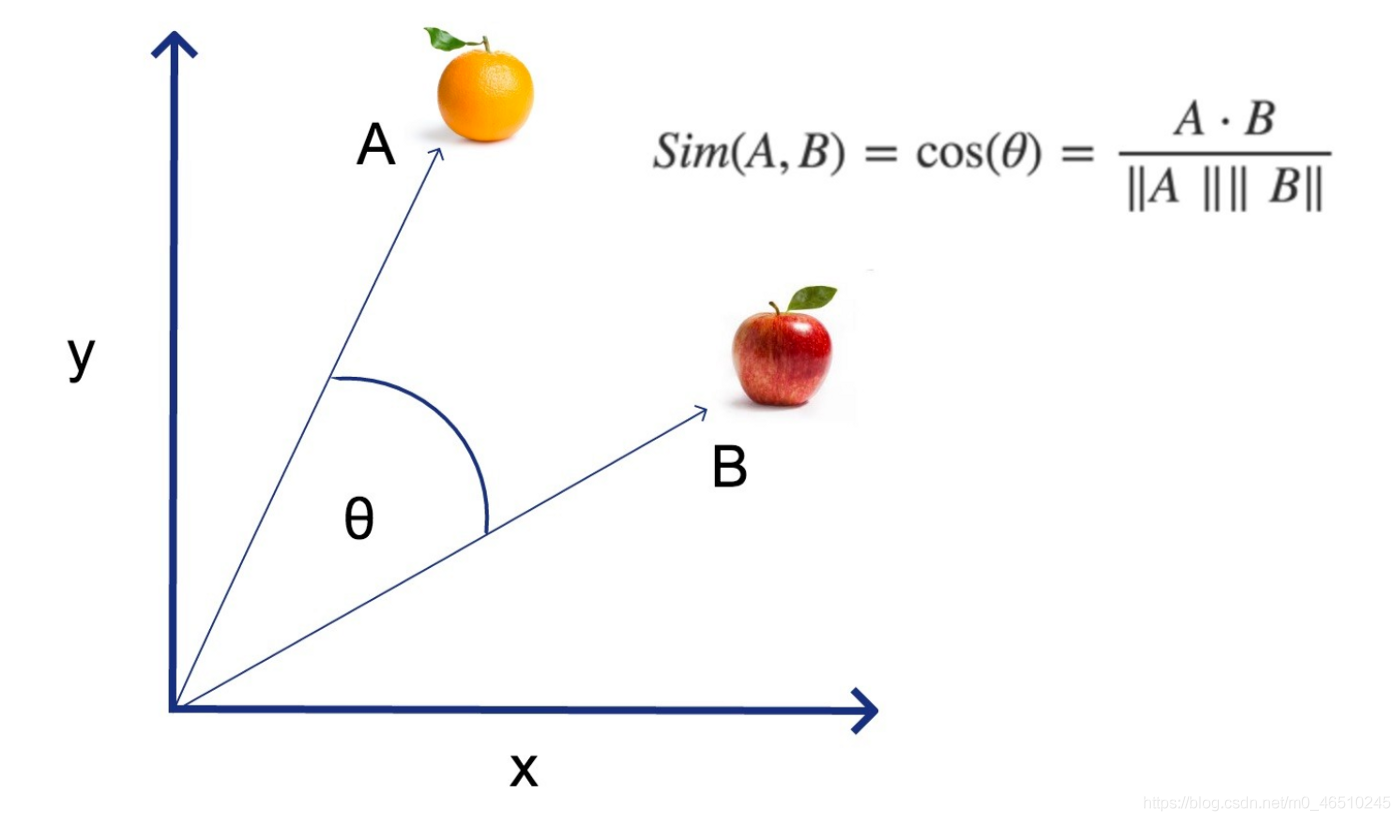
所以,在上圖中,想象一下,A線代表“閃亮的橙色水果”��,B線代表“閃亮的紅蘋果是一種水果”����。
在這種情況下��,行A和行B都對應于空格為這兩個句子創建的數字矩陣��。這兩條線之間的角度——在上面的圖表中由希臘字母theta表示——是非常有用的!你可以計算余弦來判斷這兩條線是否指向同一個方向。
這聽起來似乎是顯而易見的��,難以計算��,但關鍵是����,這種方法為我們提供了一種自動化整個過程的方法�����。
總結
回顧一下�����,我已經解釋了遞歸python函數如何使用余弦相似性和spacy自然語言處理庫來接受相似文本的輸入,然后返回彼此不太相似的文本�����。
可能有很多這樣的用例……類似于我在本文開頭提到的歸檔用例��,你可以使用這種方法在數據集中過濾具有惟一歌詞的歌曲�����,甚至過濾具有惟一內容類型的社交媒體帖子。
到此這篇關于利用Python過濾相似文本的簡單方法的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關Python過濾相似文本內容請搜索腳本之家以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持腳本之家����!
您可能感興趣的文章:- python使用jieba實現中文分詞去停用詞方法示例
- Python實現敏感詞過濾的4種方法
- Python過濾序列元素的方法
- python numpy實現多次循環讀取文件 等間隔過濾數據示例
- python正則過濾字母、中文����、數字及特殊字符方法詳解
- python基礎之停用詞過濾詳解